Powering Connectivity in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
By Colin Davies, European Applications Manager
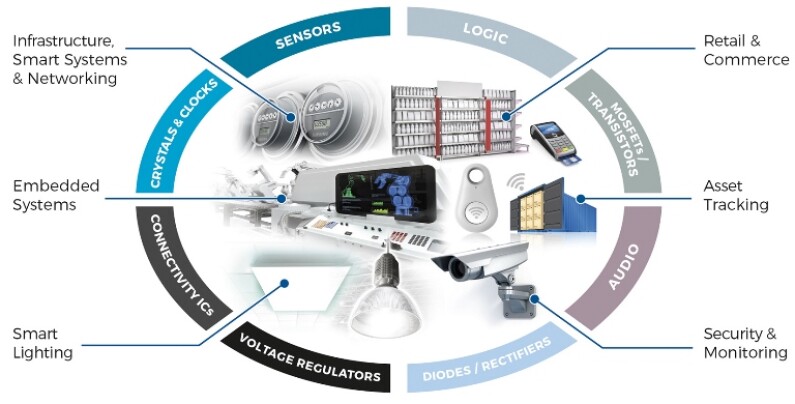
IoT is the drive for what is an ‘EoT’ event, the ‘Electronification’ of Things. IoT simply means that an object has a web addressable link; what you can do with that interconnectivity is driving the huge boom in the electronics sector.
Home automation, which covers heating, lighting, security and energy monitoring, allows remote control via a wide range of interconnected devices, from watches to smart phones, tablets to computers.
The online storage and access of massive amounts of data coupled with high-speed connectivity is enabling online entertainment and social media platforms to change our viewing habits. Instantaneous gratification requires high speed data rates, an area in which Diodes Incorporated has enabling solutions.
A common concern with all IoT connected devices is safety and security, from the loss of personal data to losing control of power stations. The willingness of IoT connected devices to talk to one another must be countered by evermore sophisticated security solutions applied at the hardware and software level.
The increased use of various sensors, from optical, distance, heat, Global Positioning Systems (GPS) and particularly Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMs), means more of these ‘things’ can be monitored and controlled remotely. Electronics is the enabling technology for the EOT, but the differentiation lies in the software, which is becoming increasingly more abstract.
Diodes’ strength has always been in developing efficient power management technologies, which all IoT systems require in order to maximize their operating times and effectiveness. While Diodes is well established in providing these enabling technologies covering power management and protection circuitry, recent acquisitions have allowed us to also address the high-speed data area. This means we now provide competitive solutions in application areas previously not serviced by Diodes.
Smart Metering
The monitoring and reporting of utilities (gas, water and electricity) has been enhanced by the IoT; the inclusion of an IP address and connection to the Internet as allowed remote reporting of energy by suppliers and consumers alike. Connectivity allows all manner of devices to report their energy and water usage.
Diodes plays a huge role in smart metering, from developing efficient and small power supplies to providing highly accurate clocks and crystals, as well as tamper proofing technologies. Efficiency is key here, as the meter is on 24 hours a day and although the power used is usually small in comparison to the energy measured, it must as insignificant as possible.
Electricity meters have been tampered with for decades to misreport the energy used by showing a value much lower than the actual energy used. This is usually achieved by placing magnets near the meter, which interrupt or otherwise alter the current measured. Diodes produce magnetic sensors that can be used to detect the presence of a magnetic field. If a magnetic field is detected, the smart meter can take the appropriate action, such as reporting that it has been tampered with via the Internet. The circuitry used to measure the meter’s current is very sensitive and needs to be accurate over a wide range of tens of milliamps to 100s of amps. The detection of any magnetic field intended to disrupt this sensitive interface must operate in three dimensions.
Meters located in industrial remote installations are often battery operated, so energy efficiency and low power are essential in order to maximize battery life. Connected devices like remote meters need to be designed with power consumption as a priority.
Smart Connected Lighting (SCL)
SCL is another IoT market that is growing, from consumer to industrial, public and private. By making lighting IP addressable, it allows the lamps to be controlled remotely and centrally, maximizing energy efficiency.
As SCL lamps may operate in a passive listening state for long periods, standby power consumption is a key factor for designers, as is meeting all legislation. Diodes has been addressing LED lamps for more than 10 years and has introduced solutions optimised for high power efficiency and density even during standby. Another area that is important for both consumers and industrial applications is a phenomenon commonly called ‘eflicker’; invisible to the human eye, eflicker disrupts image capture equipment, such as security cameras. It occurs when Pulse Width Modulation (PWM; a switching on and off technique) is used to dim the LEDs, either for brightness or colour control. The lamp is effectively being turned off for short periods of time (100s of µs), which is long enough for a CCD/CMOS image sensor to capture an image without light.
To address this issue, Diodes have developed SCL solutions that use higher PWM frequencies, which reduces the period of off-time and thereby mitigates the ‘eflicker’ phenomenon.
